Utilization of Solar Panels
Solar panels can be used for numerous applications, broken down into 2 categories:
“Grid-connected” applications and Remote areas applications.
1) Grid-connected” applications”
Photovoltaic panels are integrated into buildings, thus coupling PV energy with the Electricity Board power supply network.
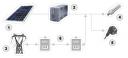
1. Photovoltaic modules 2.Inverters 3. Network 4.Lighting
5. Household applications
6. Energy metering < produced by the customer
> supplied to the customer
Direct current from the solar modules is transformed into alternating current via an invertor, which can then be directly used to supply power to the electric appliances in a building. The surplus supplied by the panels is sent onto the grid and resold.
Remote areas applications
– Remote sites: lighting, radio, television, small household appliances
– Public lighting: advertising signage, bus shelters
– Rural electrification
– Pumping
– Telecommunications: infrastructure, GSM relays, remote subscriber station
– Signage: road signs, maritime beacons, radio, television

1. PV modules 2. Regulation charge/discharge, storage batteries
3. Lighting 4. Refrigeration 5. Household appliances
The installation power supply is independent, i.e. there is no connection to the grid.
LPV modules convert sun rays into direct current. The electricity produced is stored in a battery. When there is insufficient sunshine and light, at night for example, the battery restores the power needed for the installation to function. A regulator protects the battery.